2026-02-02
Neurogenic Bladder (NB) is a common complication after spinal cord injury. The common symptoms include urinary retention and increased residual urine volume. Intermittent catheterization refers to the method of inserting the catheter through the urethra into the bladder at regular intervals to ensure regular bladder emptying. Intermittent catheterization is the preferred method recommended by the International Continence Society to assist patients with NB in emptying their bladders. It is currently the "gold standard" for bladder emptying in patients with spinal cord injury and can effectively maintain bladder capacity.
In clinical practice, during intermittent catheterization, complications such as urethral bleeding, bladder stones, and urinary tract infections often occur due to improper operation, forceful insertion, and non-standard disinfection. At the same time, for most patients with NB, after discharge, due to the lack of relevant knowledge about intermittent catheterization, the caregivers have limited care capabilities, and the nursing quality is poor. As a result, patients are prone to urinary tract injuries and urinary tract infections, which are complications of the urinary system.
With the deepening of the concepts of precision and holistic care, the total management model has certain application prospects in clinical nursing management. It refers to upgrading from a single patient treatment to a comprehensive management model covering pre-hospital preparation - in-hospital treatment - and post-hospital extension, which is a new concept and treatment strategy.
The intermittent catheterization full-process management model involves adopting the standardized intermittent catheterization management process upon admission, providing remote intermittent catheterization management guidance to patients through groups after discharge, and conducting follow-up visits at the outpatient clinic 3 months later.
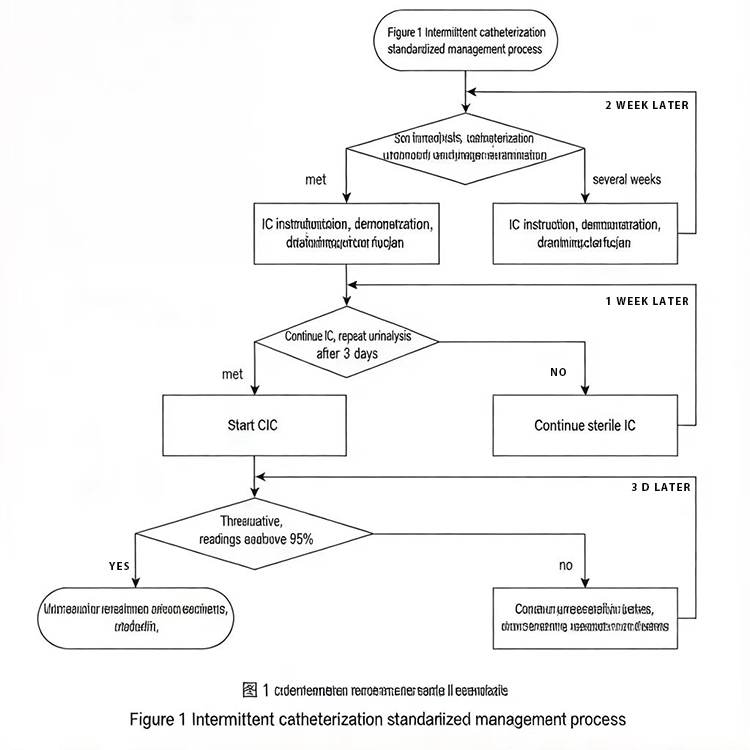
The continuous management model of intermittent catheterization can help patients and their caregivers master the standardized intermittent catheterization procedures, enhance the bladder management capabilities of patients and caregivers, thereby maintaining periodic bladder emptying and dilation, maintaining the physiological state of the bladder, promoting bladder function recovery, reducing the incidence of related complications caused by indwelling catheterization, alleviating economic burdens, improving patients' satisfaction, and enhancing the quality of life of patients.
The content of this article is sourced from the internet. The author assumes no responsibility for it. Without permission, copying is strictly prohibited.
|

浙公网安备33021202001967号